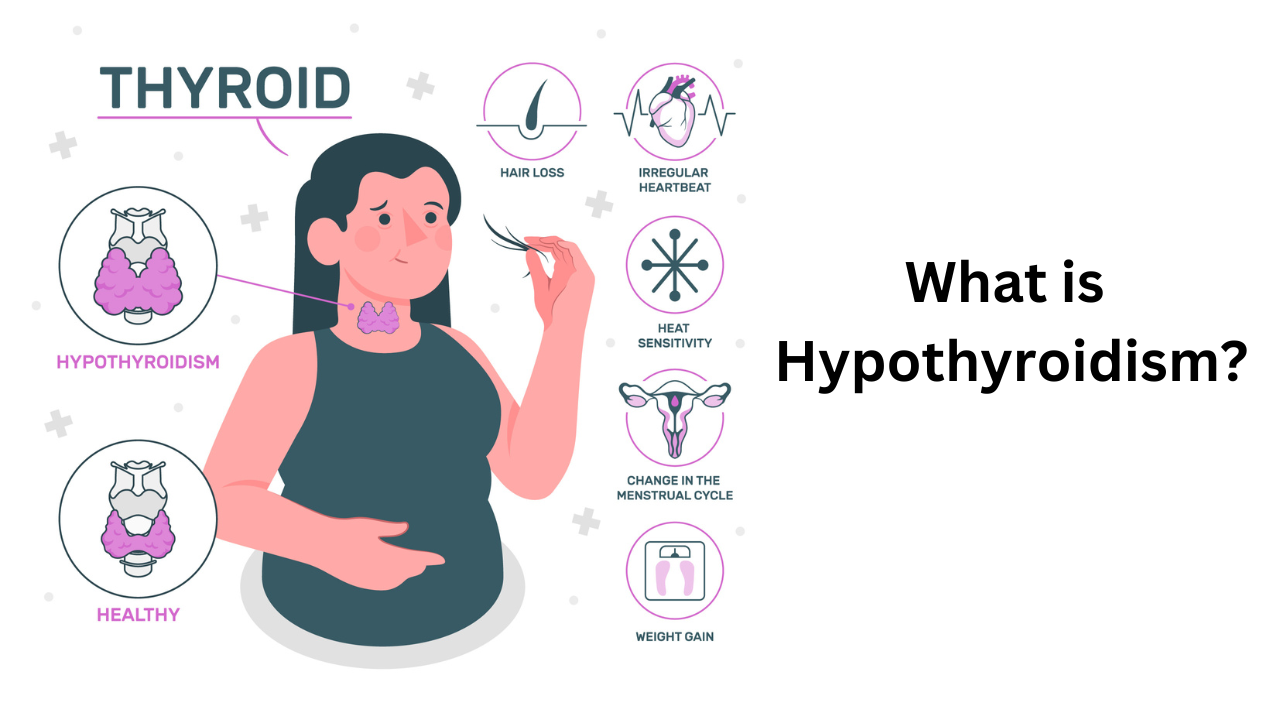
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism, energy production, and overall growth and development. Here are some key points regarding hypothyroidism:

What is the Signs and Symptoms Hypothyroidism?
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair
- Constipation
- Muscle aches and joint pain
- Depression or mood swings
- Impaired memory and concentration
- Irregular or heavy menstrual periods
- Slow heart rate
Causes of Hypothyroidism:
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is the most common cause, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
- Surgical removal of the thyroid gland or radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism.
- Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone.
- Congenital hypothyroidism (present from birth).
- Pituitary gland dysfunction or hypothalamic disease.
Complications:
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland due to constant stimulation by the pituitary gland.
- Heart problems: Hypothyroidism can lead to an increased risk of heart disease, including high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and an enlarged heart.
- Mental health issues: Depression, cognitive impairment, and memory problems may occur.
- Infertility and pregnancy complications: Untreated hypothyroidism can affect fertility and increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and developmental issues in the baby.
- Myxedema: A severe form of hypothyroidism characterized by extreme fatigue, low blood pressure, and decreased body temperature.
Prevention of Hypothyroidism:
While some causes of hypothyroidism cannot be prevented, here are some measures you can take to maintain thyroid health:
- Iodine intake: Ensure an adequate intake of iodine, as it is an essential nutrient required for thyroid hormone production. It is found in iodized salt, seafood, dairy products, and some fruits and vegetables.
- Proper nutrition: Maintain a balanced diet with a variety of nutrients to support overall thyroid function.
- Regular check-ups: Periodic thyroid function tests can help detect any abnormalities early on.
- Minimize radiation exposure: Protect yourself from unnecessary radiation exposure, particularly around the neck region.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can affect thyroid function, so it’s important to adopt stress management techniques like exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques.